Can You Connect VGA to Displayport? Is It Properly Workable?
The world of display technology has evolved significantly over the years, moving away from older video standards like VGA (Video Graphics Array) towards newer, high-definition standards such as DisplayPort. However, there may still be situations where you need to connect a device with a VGA output to a monitor or projector with a DisplayPort input.
In today’s post, we’ll explore how you can bridge the gap between these two technologies, the reasons behind them, the steps involved, potential issues, and how to troubleshoot them.

Why Connect VGA to DisplayPort?
Before diving into the technical aspects, let’s discuss the reasons you might want to connect VGA to DisplayPort. VGA is an older analog video interface commonly found on older laptops, desktops, and other devices. On the other hand, DisplayPort is a modern digital video interface that offers better image quality and supports higher resolutions and refresh rates. Here are some common scenarios where you might need to make this connection:
Legacy Devices: You have a legacy device with a VGA output, and the only available display you want to connect it to uses DisplayPort.
Compatibility: Your primary device supports both VGA and DisplayPort, but you need to connect it to a DisplayPort-only display.
Cost-Efficiency: You want to avoid purchasing a new monitor or projector with VGA compatibility and instead use an adapter.
Can You Connect VGA to DisplayPort?
Yes, it is possible to connect VGA to DisplayPort, but it’s important to understand that these two interfaces have fundamental differences:
- VGA is an analog signal, while DisplayPort is digital.
- VGA supports lower resolutions and refresh rates compared to DisplayPort.
- To bridge the gap, you’ll need an adapter or converter to convert the VGA analog signal to a digital format compatible with DisplayPort.
How to Connect VGA to DisplayPort
Here are the steps to connect VGA to DisplayPort:

Obtain the Right Adapter: Purchase a VGA to DisplayPort adapter or converter. Ensure it is compatible with your devices and supports the resolution and refresh rate you desire.
Connect VGA Cable: Plug one end of the VGA cable into your source device’s VGA output.
Connect the Adapter: Plug the VGA side of the adapter into the VGA cable and the DisplayPort side into your DisplayPort input on the monitor or projector.
Power On and Configure: Power on your devices and configure the display settings on your source device, if needed.
Check for Signal: Ensure you have a stable video signal on your DisplayPort-enabled display.
Why It Might Not Work and How to Fix It
Connecting VGA to DisplayPort might not work for several reasons. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
Incompatible Adapter: Ensure you have the right adapter. Some adapters only work in one direction (VGA to DisplayPort), so double-check compatibility.
Resolution/Refresh Rate Mismatch: If the source device’s resolution or refresh rate is not supported by the adapter or display, you may encounter issues.
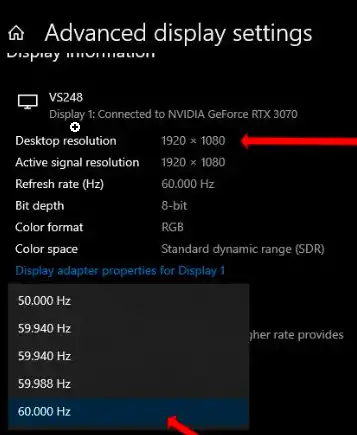
Adjust the settings on your source device to match the display’s capabilities.
Power Supply: Some adapters require additional power to function correctly. Check if your adapter needs an external power source and connect it accordingly.
Driver Updates: Ensure your device’s graphics drivers are up to date, as outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues.
Cable Quality: Poor-quality VGA cables or DisplayPort cables can also cause problems. Swap out the cables to rule out this issue.
Firmware Updates: In some cases, the monitor or projector may require a firmware update to work with certain adapters.
Hardware Compatibility: There may be some devices that simply cannot be successfully connected due to inherent incompatibility.
To Sum Up
Connecting VGA to DisplayPort can be a viable solution in certain situations, allowing you to make use of older devices with newer displays. While it is technically possible, ensure that you have the right adapters, understand the limitations of the technology, and are prepared to troubleshoot any potential issues that may arise. With the right setup and some patience, you can bridge the gap between these two video interfaces and continue to use your legacy devices with modern displays.
Subscribe to our newsletter
& plug into
the world of technology