What is Overclocking? How to Overclock CPU [A to Z Guide]
Have you ever felt if your PC would run a little faster, then it would be awesome? If the answer is yes, this article is going to give a guidance to fulfill your desire. It is a common question in the tech world that how to overclock CPU? Though the procedure to overclock a CPU is not an easy task, but it is not a hard one too. Follow this overclocking guide till the end. At the end of the guide, I hope you’ll be using the same PC you had before but a little speedy than before!

What is Overclocking?
Overclocking a CPU means manually boost up your CPU which it was not intended to be by default. You might wonder how that can be possible. Overclocking means making your CPU run faster. It means you can change the voltage supply to the processor manually to work faster. The ability to run faster is already there. By default, the manufacturer like Intel and AMD restricts the CPU’s performance to run it at a safe level to ensure the reliability for a longer time. Though you have your own choice to run your CPU a little faster by just changing a few settings, there are risks too.
Why Overclock?
If you don’t want to buy new components by spending money on your PC but want your PC work a little faster, then there is an option which is fully free of charge! That is overclocking. You can have a little faster computer than before though having the same components as before. Though you can overclock your CPU, you can overclock RAM and GPU too. But in this article, we will discuss overclocking a CPU as well as a little about overclocking RAM.
Do you Need Overclocking Your CPU?
If you have faster CPU than you probably will not feel the lack of speed. But if you run on a slow CPU like a dual-core CPU, then you’ll feel the difference between the overclocked and un-overclocked CPU. The choice is yours. But overclocking your CPU is a little fun, right? If you are a gamer or a graphics designer who generally use power-intensive software like Solid Works, Photoshop, illustrator, then we recommend you to overclock your CPU and RAM.
What You Need to Overclock
You can overclock your RAM, CPU, GPU. But in this article, we are going to give a guidance to overclock your CPU and RAM.
Things To Remember Before Overclocking
Overclocking is not same for all the chipset. For example, suppose you have a Devil Canyon or Ivy Bridge chipset, they have different ways of overclocking the CPU. If you are looking for achieving the highest possible overclocking on your chipset, you can follow a dedicated guide for overclocking your chipset and processor.
A processor can be overclocked only if it is unlocked. For example, suppose you have a non-K Intel Core i7 processor which has a locked clock speed, that means it is preventing you from overlocking it or you may have an unlocked-K version of its Intel Core i7 processor which allows you to overclock the processor.
If you overclock your CPU, you lose the warranty provided by the manufacturer of your CPU. But there are some companies which allow overclocking by not voiding the warranty. Again, if you don’t overclock the CPU perfectly, then there is a chance of damaging the component.
Necessary Tools to Download
In order to test your overclocking results properly, you have to download a few benchmarking and stress test tools. These programs will test the performance of the processor and will check its ability to maintain that performance over time.
- CPU-Z : This simple program will monitor overclocking by which you’ll be able to see quickly your clock speed and voltage in Windows. But it doesn’t do anything in overclocking. But it is so helpful to ensure you that everything is working perfectly.
- Prime95: This is another benchmarking program that is generally used for stress testing. This is designed to run for long periods.
- LinX – This is also a stress testing program. This is lighter than Prime95. So, it is good for testing between each change is done.
Checking Motherboard and Processor
As you already know that all the motherboards and processors are not same. They have different capabilities in terms of overclocking. There are also some differences between AMD and Intel when it comes to overclocking. But the general process is same for all. The biggest thing you have to look for is whether your multiplier is unlocked or not. Suppose the multiplier is locked, the only thing you will be able to do is to adjust the clock speed which doesn’t provide perfect result.
- Check your PC’s documentation. You will find there whether your motherboard support overclocking or not.
- Some CPUs are designed to be overclocked. So, they work better than others. Check your CPU’s capability.
Baseline Stress Test
Before overclocking, you have to use baseline settings in Prim95 to run a stress test which will show you a baseline comparison against starting the overclocking. You can run a stress test of your GPU too. This will also show if there is any problem with the base in the settings.
- Check the temperature levels during the stress test. If your CPU’s temperatures are above 70 °C, you will not be able to gain much benefit out of overclocking. Because the temperature will rise high during overclocking and thus damage your CPU. Then, you have
To install a new heatsink or apply thermal paste.
- Your system may crash during the baseline stress test. It means there is an issue with the hardware which needs to be found out before starting overclocking.
Start Overclocking
1. Increase Base Clock
Go to BIOS: During overclocking, you are going to make the majority of the changes in your computer’s BIOS. Bios is the configuration menu for your PC. It can be accessed before the operating system is loaded. Most Bios can be accessed by holding the ‘del’ key while the computer is booting up. There are other possible setup keys like ‘F10’, ‘F12’, ‘F2’.
All the BIOS’ are different. So, menu labels and locations can vary from system to system. Don’t be afraid to go into the system to find out what you need.

Open the Voltage(frequency) Control
This menu can be labeled as “Overclocking” too. In this menu, you will have to spend most of your time. It will allow you to adjust the CPU’s clock speed and the voltage it receives. Go to the Advanced frequency settings.
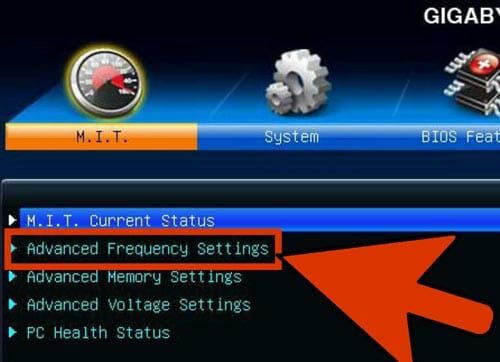
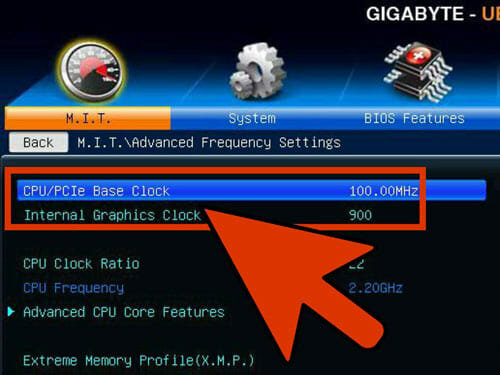
Increase the Base Clock by 10%
The base clock is referred to as the front side bus or bus speed. It is the base speed of the processor. It is a lower speed which is multiplied by reaching the total core speed. almost all the processors have the ability to handle a 10% jump at the start. Suppose, the base clock is 100 MHz and the multiplier is 16. Then, the clock speed is 1.6 GHz. Increasing it up to 10% will make the base clock 110 MHz. So, the clock speed will be 1.76 GHz.
Run a Stress Test
As soon as you have performed the initial 10% raise, restart the computer. Then boot into your PC’s operating system as before. Start the Linux software and run it through a few cycles. If there is no problem, you may move on. But if the system is still unstable, then you won’t be able to get much improvement out of the overclock. If it is the condition, you have to reset the settings to default.
Increase Base Clock Until the System Becomes Unstable
Don’t increase 10% each time. You now reduce the increments to about 5-10 MHz per pass. You should run the benchmark test each and every time you make a change in order to reach an unstable state. The instability is caused by not receiving enough power by the processor.
If the motherboard does not permit you to adjust the multiplier, you can just repeat the increasing of the base clock. If you have permission to adjust the multiplier, you can move on to the next section. Record the settings you are currently at and the changes you are making.
2. Overclock by Raising the Multiplier
Lower the base clock
Before start increasing the multiplier, you should lower the base clock a little to make the multiplier increases more precisely. A combination of a lower base clock and a higher multiplier is a more stable system. But a combination of a higher base clock and a lower multiplier will lead to more performance. It is our job to find the best combination to attain the perfect goal. Do it as like before.
Raise the multiplier
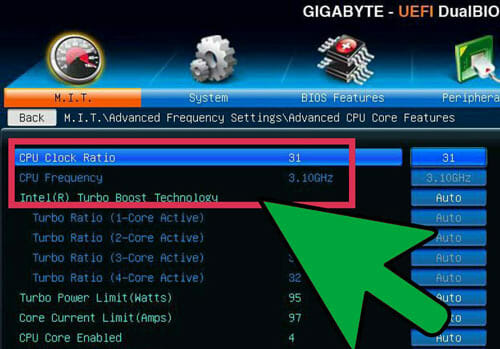
If you’ve already dropped the base clock a bit, you can start raising your multiplier. Start raising the multiplier in 0.5 increments. The multiplier is generally called CPU Ratio or something similar. You may find it set to Auto when you first encounter it.
Run a stress test
As soon as you have performed raising the multiplier, restart the computer. Then boot into your PC’s operating system as before. Start the LinX software and run it through a few cycles. If there is no problem, you may increase the multiplier again. Keep it in mind that every time you raise the multiplier, you have to run a stress test.
Check the temperatures
You must pay attention to the temperature level during the overclocking process. You can hit a temperature limit before the system becomes unstable. If this happens, you may have reached the overclocking limits. Then you have to find the best combination of base clock and multiplier.
Every CPU has different safe temperature range. Generally, you should not allow your CPU to reach the 85 °C.
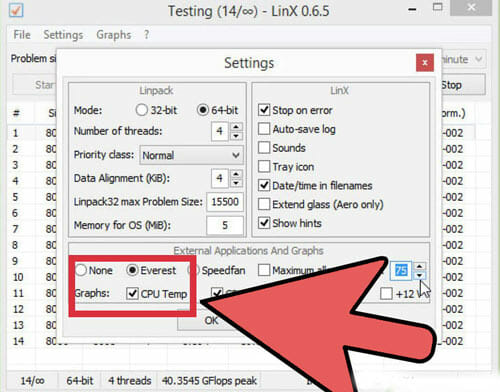
Repeating the Previous Procedure Until the Upper Limit is Reached
Do this several times. After that, you should now have settings that have caused your PC to become unstable. As long as the temperature is within the safe limit, you may now start adjusting the voltage levels. It will allow you to reach further increases in CPU speed. So much fun isn’t it!
3. Voltage Raising
Raising CPU Core Voltage
This is generally referred to as Vcore Voltage. But raising the voltage beyond safe limits may damage your equipment. So, this task is the most tricky and dangerous part of the overclocking procedure. Your CPU and motherboard can handle voltage increases up to a limit. Every CPU and motherboard has their limit but it is not same for all. So, pay some extra attention to this task. Start raising the core voltage. Increase the voltage in 0.025 increments. the value is relatively low because there is a risk of jumping the temperature too high.
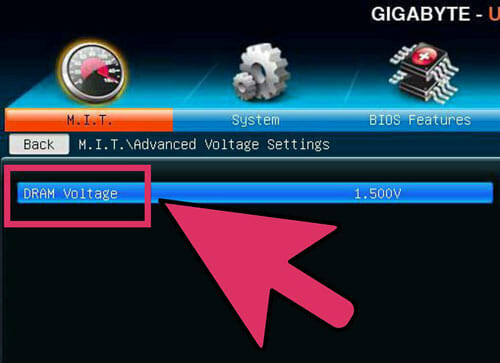
Run a stress test
After the first increment of the voltage, run a stress test. You may remember that you left the system in an unstable state in the previous section. So, now you may hope for a stable stress test run. If you find your system stable, you should make sure that temperatures are still at the safe level. If your system is still unstable, lower either the base clock speed or the multiplier and run the stress test again.
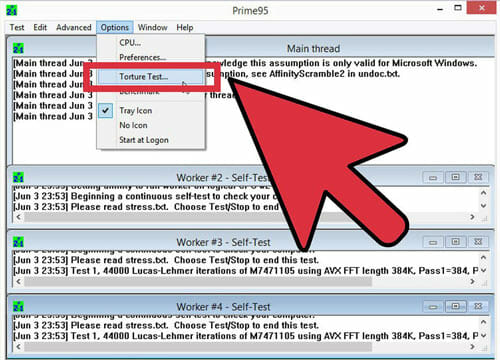
Return to overclock base clock or the multiplier section
As soon as you have managed to make the unstable system stable by increasing the voltage, you may now go back to increase either the base clock or the multiplier. Increase them in the same small amount like before. Then run the stress test. Continue the procedure until the system becomes unstable again.
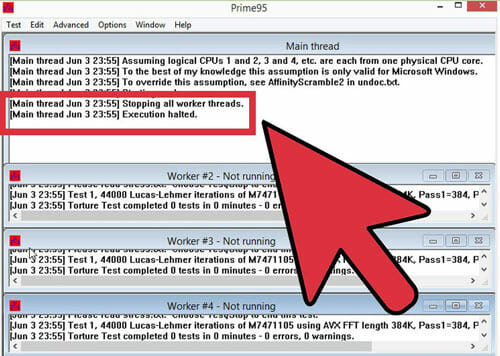
Increasing the voltage increase the temperature most. To get rid of this problem, maximize the base clock as well as the multiplier in order to gain the best performance. So that the given voltage has the minimum value. So, you must have the patience for achieving the best result by overclocking because there is a lot of combination possible.
Repeat the Cycle to Reach the Maximum Voltage or Maximum Temperature
After some time, you will find a point where you’ll not be able to get anymore increases, or you may find the temperature to an unsafe level. This will be the limit of your motherboard and the processor. Generally, you should not raise the voltage more than 0.4 above the original level. Raising above 0.2 is good.
If you find that the temperature is beyond safe limit before reaching the acceptable voltage increase, you may pay some money to install a heatsink or cooling paste.
4. Final Stress Testing
The last Safe Settings
Now, lower the base clock or multiplier to the last working settings. This is the new processor speed. If you’re lucky it will be seen larger than before. If everything boots ok, then your PC is ready for the final test.
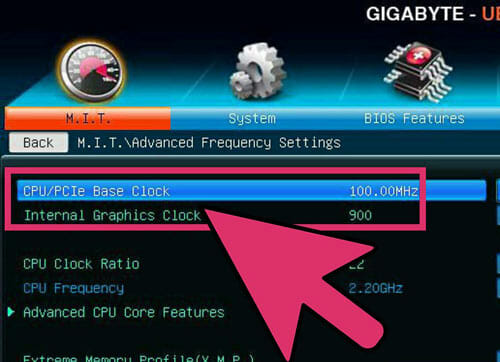
Memory Speed Increase
Now, raise the memory speeds towards their initial levels. You should do this slowly, do stress testing as you go. In this level, you might not be able to raise them back to their original levels
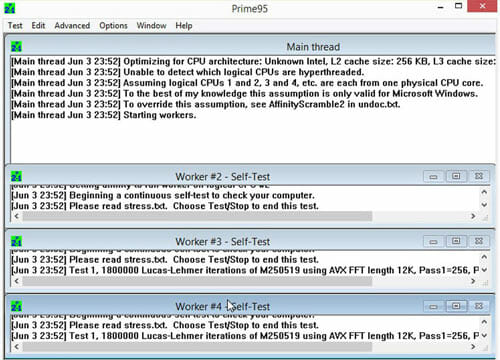
Running a Long Stress Test
Now, open Prime95. Run the stress test for 12 hours. You may think it is a long time. But you should think about the stability for a long time. This action will ensure a better and more reliable performance. The system may become unstable during this test, or the temperature may reach unacceptable levels. If it happens, you will have to go back and then, you have to readjust the clock speed and the multiplier and the voltage like you have done before.
After opening Prime95, select Just Stress Testing. Then select Options, then select torture Test and last, set it to small FFT.
Upper-level temperature is OK because Prime95 pushes the PC more than most programs. But above all, we suggest that your idle temperature should not rise above 60 °Celsius.
Real life Testing
You have already done a lot of stress testing. But in real life, you will face the various problem. Though stress test programs like Prime95 are great for making sure that you are running a stable system, now you should make sure that your PC can handle random real-life situations. You may or may not be a gamer, just start the most intensive game you know which lag in your PC. If you play video, just play a blue-ray high-resolution video. Make sure that everything works perfectly as it should. Now, it should work even better!
Summing Up
You may use a powerful CPU or not. Suppose you use your PC roughly. Whether you use a powerful CPU or not, you may feel sometime if your PC would run faster! But you may not want to pay money to buy another CPU. Then you can make your CPU much faster than before just following some steps which are known as overclocking. How to overclock your CPU? This overclocking guide has already given the solution for your problem. If you have already gone through the whole article and followed it, then I hope, you are reading this section with a much faster PC!
- What is Overclocking?
- Why Overclock?
- Do you Need Overclocking Your CPU?
- What You Need to Overclock
- Things To Remember Before Overclocking
- Necessary Tools to Download
- Checking Motherboard and Processor
- Start Overclocking
- 1. Increase Base Clock
- 2. Overclock by Raising the Multiplier
- 3. Voltage Raising
- 4. Final Stress Testing
- Summing Up
Subscribe to our newsletter
& plug into
the world of technology