Decoding Your Router Lights: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Status Indicators
When it comes to setting up and troubleshooting your home network, your router is the heart of your internet connection. For most of us, the router sits quietly in the corner, flashing lights that are mostly ignored until something goes wrong. But those blinking lights are more than just decoration—they serve as critical indicators that can tell you everything you need to know about your internet connection, network health, and even security status.

In this guide, we will break down the common status indicators on your router, what they mean, and how to use them to troubleshoot any potential issues.
1. What are Router Status Lights?
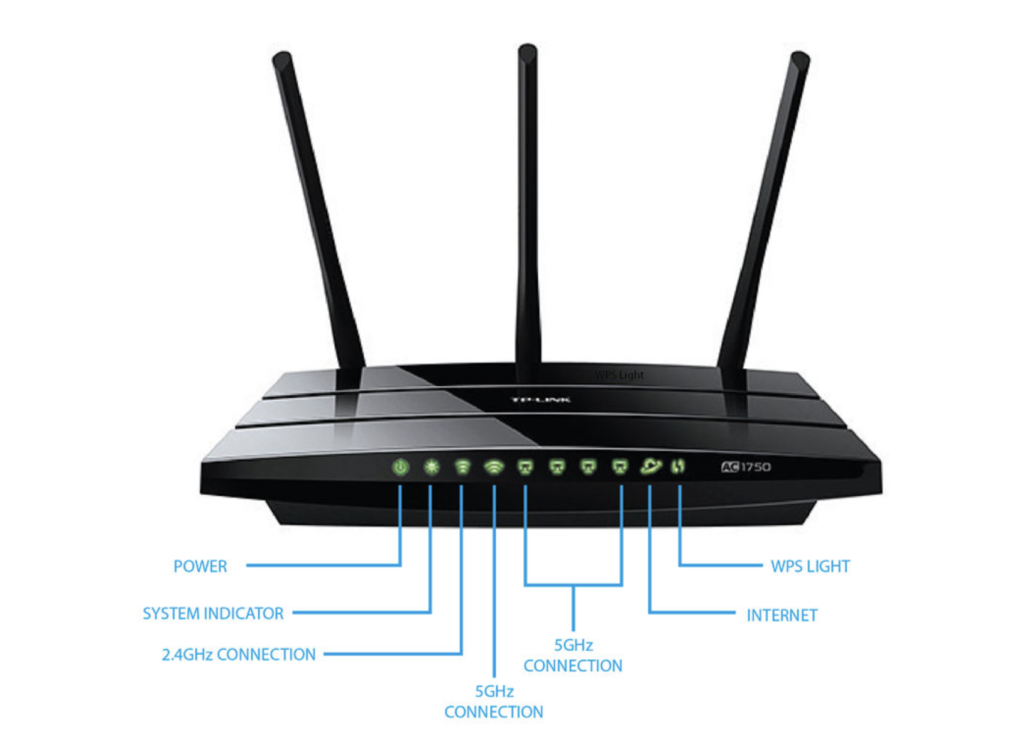
Router status lights, often referred to as LED indicators, are small lights on the front panel of your router. These lights help users understand the operational state of the device and its various components. Typically, these lights correspond to various router functions such as power, connectivity to the internet, wireless network activity, and more.
Although different router models may have slightly different setups, most modern routers follow a similar system of color codes and flashing patterns.
2. Key Router Lights and Their Meanings
2.1 Power Light
- Solid Green or Blue: The router is powered on and functioning properly.
- Off: The router is turned off or is not receiving power. Check if the power cable is securely plugged in and the electrical outlet is functioning.
- Flashing Green or Blue: The router is booting up. This is usually normal when the router is first powered on or after a reset.
- Red or Amber: The router is having trouble powering on. A red or amber power light typically indicates a fault in the router hardware or a power supply issue.
2.2 Internet/ WAN Light
- Solid Green or Blue: Your router is successfully connected to the internet through the WAN (Wide Area Network) port, meaning that the connection to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is active.
- Flashing Green or Blue: Data is actively being transferred between the router and the internet. This typically happens when you’re browsing the web, streaming, or downloading content.
- Red or Amber: No connection to the internet is detected, which could indicate an issue with the ISP or a misconfiguration of the router’s WAN settings. Try restarting the router and checking your internet connection.
- Off: This light being off often means the router is not connected to the internet, which can be caused by an issue with the ISP or physical connections (such as a loose Ethernet cable).
2.3 Wi-Fi (Wireless) Light
- Solid Green or Blue: The Wi-Fi network is active and ready for devices to connect.
- Flashing Green or Blue: Your router is transmitting data wirelessly. This will flash when data is being sent to or received from connected devices.
- Amber or Red: A potential problem with the Wi-Fi network is indicated. This could mean an issue with the wireless signal, interference, or even an overburdened network with too many connected devices.
- Off: The Wi-Fi feature is turned off or the router is not broadcasting a signal. Check the router’s settings to ensure Wi-Fi is enabled.
2.4 LAN (Local Area Network) Light
- Solid Green or Blue: A wired device is connected to one of the router’s Ethernet ports. This light indicates that the local network connection is working properly.
- Flashing Green or Blue: Data is being transmitted between a device and the router via a wired connection.
- Off: No wired devices are connected to the LAN port, or the router is not detecting a device at that particular port.
2.5 DSL/ Fiber Light (For DSL and Fiber Routers)
- Solid Green or Blue: The router has successfully connected to the DSL or fiber line, and the internet connection is active.
- Flashing Green or Blue: The router is in the process of synchronizing with the DSL or fiber network.
- Red or Amber: There’s an issue with the DSL or fiber connection, which may indicate a physical fault in the line or misconfiguration.
- Off: The router is not detecting the DSL or fiber signal at all. This can happen if the line is down or not properly connected.
2.6 USB Light (If Applicable)
Some routers have USB ports that allow you to connect external devices like hard drives or printers.
- Solid Green or Blue: The connected device is recognized and working.
- Flashing Green or Blue: Data is being transferred to or from the external device.
- Off: No device is connected or the connected device is not recognized.
3. Understanding Flashing Patterns and Their Significance
Flashing lights on your router often carry important information beyond just the color. The pattern of flashing—such as whether the light is blinking steadily or rapidly—can provide more specific insight into the router’s state.
- Slow Flashing (e.g., once every few seconds): This typically indicates that the router is performing background tasks such as booting up, syncing with the network, or updating firmware.
- Rapid Flashing: Rapid flashing often indicates activity—either data transfer between the router and devices or an issue where the router is trying to reconnect to the internet or a wireless network.
- Alternating Flashing: On some models, different lights may alternate in flashing patterns to indicate a problem with a particular network service (such as internet connectivity or Wi-Fi broadcasting).
4. Troubleshooting Your Router Using the Lights
Now that you understand the meanings behind the different lights on your router, you can use them to troubleshoot issues more efficiently. Here are some common scenarios where the router’s lights can help guide you to a solution:
4.1 No Internet Connection
If the internet light is off or red, your router isn’t able to connect to the internet. Follow these steps:
- Check all physical connections, including the power cord and Ethernet cables.
- Restart your router by turning it off and back on.
- If the issue persists, check for any outages with your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or try resetting the router to factory settings.
4.2 Wi-Fi Issues
If the Wi-Fi light is off, your wireless network might be turned off. You can turn it back on by logging into the router’s admin interface or using the physical Wi-Fi button (if your router has one). If the Wi-Fi light is amber or red, there might be interference or too many connected devices. Consider reducing the number of devices on the network or changing the Wi-Fi channel.
4.3 Slow Internet or Connectivity Fluctuations
Flashing or blinking WAN and Wi-Fi lights could indicate data transfer or network congestion. Try disconnecting unused devices from the network to reduce load. If you notice slower speeds, check the router settings for a possible firmware update or channel adjustment.
5. Other Common Router Lights and Their Meanings
Some routers come with additional status lights for specialized functions:
- Firewall Light: Indicates the status of the router’s built-in firewall. If this light is off or flashing red, it may indicate a security issue.
- WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) Light: This light usually flashes when you’re in the process of connecting a new device via WPS. A solid light indicates a successful connection.
6. Conclusion
The blinking lights on your router may seem trivial, but they are important signals that offer critical information about the state of your network and help you troubleshoot problems effectively. By familiarizing yourself with these indicators, you can quickly identify and solve network issues without needing to contact your ISP or a technician.
So, next time you notice a flickering light on your router, take a moment to understand what it’s trying to tell you—it could save you time and frustration in resolving network issues!
Subscribe to our newsletter
& plug into
the world of technology